Breast Surgery
Gynecomastia
Videos
Your First Appointment
Diagnostic Tests
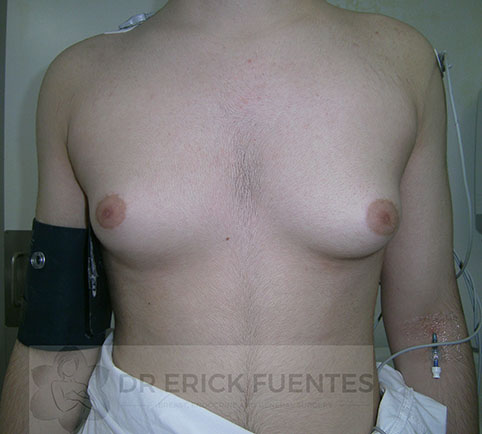
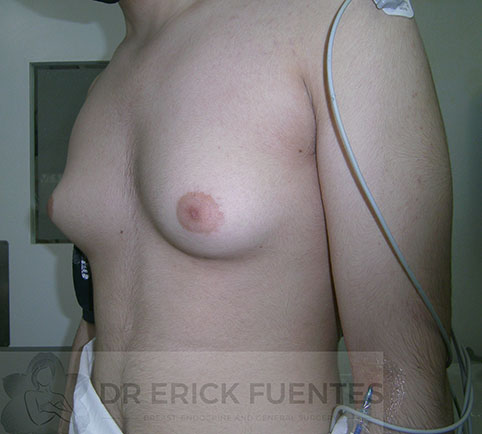
Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is the name given to enlargement of the breast tissue in males. It is caused by a relative imbalance between androgens (“male” hormones) and oestrogens (“female” hormones).
Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts. This condition may be seen in newborns, adolescents and elderly individuals, as a part of physiological changes. It is sometimes, but not always, painful with an associated lump behind the nipple and areola. In rare instances there may be secretion of milk from both nipples.
Generally, gynecomastia does not produce any harmful effects but it may cause undue stress and embarrassment that can impact the active sex life of the affected individual. Gynecomastia can also cause psychological damage or loss of self-esteem.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Physiological
- Newborn: Due to the presence of maternal hormones (oestrogen and progesterone) circulating in blood
- Adolescence: Due to hormonal changes during puberty that are temporary. Gynecomastia in adolescents usually disappears at the end of puberty.
- Increased age and weight: Production of testosterone declines with age while fat cells stimulate the secretion of female hormone oestrogen.
Pathological
There are various pathological causes of gynecomastia and although they may not always be the cause, they must always be excluded before any treatment. Some of the more common conditions that cause gynaecomastia are listed below.
- Increased levels of oestrogen due to various conditions such as obesity, hyperthyroidism, malnourishment, adrenal tumours and testicular tumours
- Decreased or lack of testosterone production due to conditions such as Klinefelter’s syndrome, viral orchitis and renal failure
- Chronic illness including, chronic liver disease, chronic renal failure, hypothyroidism, diabetes, malnutrition, HIV, obesity
- Endocrine disorders: hypogonadism
- Tumours of the pituitary or adrenal glands, testicle, liver, or secondary tumours.
Medications and other drugs
Certain medications and commonly used drugs cause gynaecomastia as a side effect. Some common medications that have been linked to gynaecomastia include:
- Diuretics (thiazide and spironolactone)
- Antipsychotics and antidepressants (e.g., diazepam, haloperidol, risperidone and tricyclic antidepressants)
- Heart and blood pressure meds (e.g., digoxin, verapamil, nifedipine)
- Gastric acid suppressant (e.g., omeprazole, cimetidine)
- Alcohol
- Opioids
- Cannabis
- Amphetamines
- Performance enhancing drugs: Anabolic steroids hGH, estrogens, hCG, GnRH analogs and 5-α reductase inhibitors, testosterone
- Chemotherapy agents
- Anti-androgens used in the treatment of prostate cancer
Diagnosis – Gynecomastia
The diagnosis of gynecomastia includes a physical examination of the patient, by the physician. Typically, the breasts, abdomen and testicles are examined.
Occasionally a mammogram, ultrasound and a biopsy of the breast may be needed to confirm the diagnosis. Certain blood tests may also be conducted to evaluate the underlying cause of gynecomastia.
Treatment
Non-Surgical
The non-surgical methods employed for management of gynecomastia include:
- In case of drug/medication induced gynecomastia, replacement of the offending drug with an alternative and safer medication
- Medical treatment of the underlying disease conditions
- Oestrogen antagonist drugs such as clomiphene and tamoxifen can achieve partial or complete reduction in size and tenderness in men with early gynecomastia symptoms
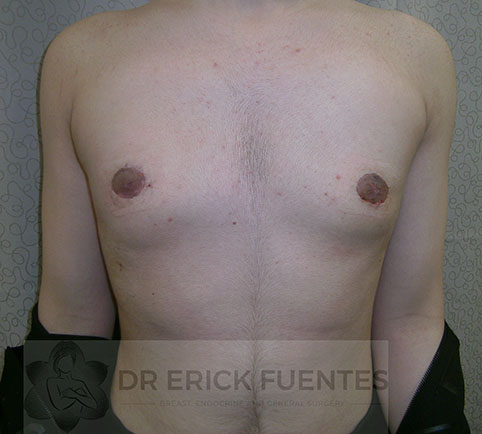
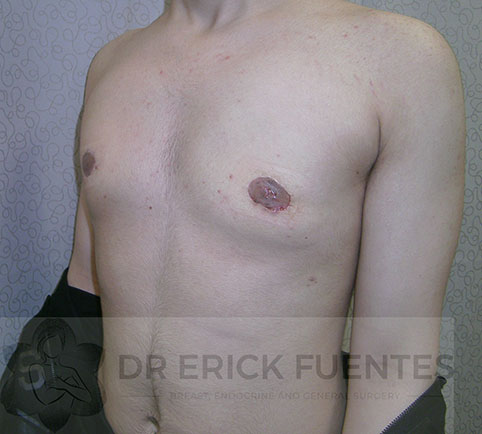
Gynecomastia Surgery
In patients not responding to non-surgical management, surgery is considered as the last option. The surgical methods for management of gynecomastia include:
- Gland excision
- Liposuction
- Skin sculpture
- Reduction mammoplasty
- Combination of the surgical techniques mentioned above
Surgery is performed under general anaesthesia. Normally the operation takes about 90 minutes, and the breast tissue is removed through an incision on the edge of the areola. Most men go home the day after surgery however some can go home the same day.
The operation does not result in much pain and most patients only need simple pain relief such as paracetamol in the post operative setting.
Loss of sensation to the nipple and the skin around it is common but varies according to the amount of tissue removed.
Before Gynecomastia Surgery
After Gynecomastia Surgery






For all appointments and enquiries, please call +61 2 8203 1359 or email info@drerickfuentes.com.au
Or contact us online using this form:
Request an Appointment Or Send a Message
Wise Medical
Level 1
11 Khartoum Road
Macquarie Park
NSW 2113
Strathfield Private Hospital
3 Everton Rd,
Strathfield NSW 2135
Hours: 9am - 5pm
Follow Us
© 2024 Dr Erick Fuentes. Breast and Endocrine Surgeon.